
"Ask Ross" is back! In this blog series, Ross Baran, Architect Design Services (ADS) representative, will answer your most pressing questions about garage doors and design. Whether you’re a seasoned architect or just starting out, Ross is here to help!
Question: Are U-factor and R-value different?
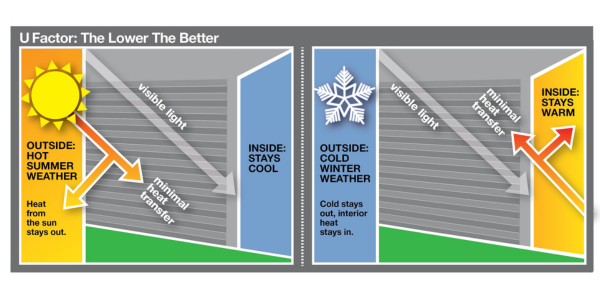

Answer: Yes, and here are the reasons why:
As an architect, you’re likely familiar with U-factor. For garage doors, U-factor measures how well an entire installed assembly rates for heat transfer. The lower your number is for U-factor, the better.
R-value is a measure of thermal resistance, in other words, the capacity of an insulating material to resist heat flow. Manufacturers will typically highlight the R-value for the center of the slat (or section) that’s best-insulated, and won’t provide any details for other parts of the slat (for example the bead of the slat), or the section. That calculation doesn’t take into account the entire installed assembly, which means that you’re not getting the most accurate rating for a door’s overall thermal performance.
The reason why R-value is misleading is because it doesn’t take the whole door into account. The calculation only highlights a specific spot on a specific component of the door. This means that the R-value can be high even if the door doesn’t actually perform well for thermal resistance. So, a higher number on a door’s R-value, doesn’t necessarily mean that the door insulates better.
Question: How do you calculate U-factor and R-value?

Answer: To measure U-factor, garage door manufacturers have to go through real-world tests by a third party, like ANSI/DASMA 105-2017. Because of these rigorous standards, you’re receiving a measurement that’s more accurate than other thermal performance ratings.
The R-value of an individual garage door section is a calculated estimate of its insulating capability. It's determined by adding up the R-values of the interior and exterior surfaces, the insulated core material, and the "air film" (the insulating effect of air on a vertical surface). Each of these components has its own unique R-value, and the sum of these values is supposed to provide an estimate of the overall R-value of the door section.
However, the calculation ignores other parts of the door section. For example, the bead is likely not insulated and would have a lower R-value. In certain doors, the insulation thickness varies across different sections. In this case you would consider the R-value at each insulation thickness and combine the values proportionally. R-value overall, is arguably a poor calculation for the thermal performance of a garage door.
Question: Do both values matter when considering thermal performance?
321c844f86346a78840eff00003b6d5a.png?sfvrsn=4b28ee6d_0)
Answer: U-factor and R-value are two measurements of a door's thermal performance, but they can't be compared. That's because they measure different things in different ways. Overall, U-factor is a better and more reliable measure of a commercial garage door's thermal performance. Why? Because it's a tested method that measures the entire door assembly. R-value, on the other hand, only estimates the thermal performance of a single door section, not the entire assembly.
If you’re not sure which type of rolling door is best for you, or would like to discuss R-value and U-factor in more detail, contact Architectural Design Services. We got you!
Ross Baran, Architectural Design Services
With five years of industry experience, Ross works with his team to support architects in the design phase. Ross and the ADS team craft project-tailored CAD drawings and specifications and provide one-on-one design support.



